Compliance in RF Circuit Boards
Electronic circuit boards need to meet EMI/EMC standards in order to operate safely. EMC stands for electromagnetic compatibility, which refers to the ability of the board to operate within an environment without generating intolerable levels of electromagnetic interference (EMI) in nearby devices and circuits. This is accomplished through design and layout techniques that ensure the board complies with EMI/EMC standards. During the rf circuit board layout stage, it is important to optimize the layout for signal integrity and power distribution as well as properly route all traces to minimize EMI emissions and susceptibility.
Several factors contribute to EMI/EMC problems in RF circuits, including internal signals that can interfere with each other, interference from external devices or radio frequency transmissions and noise from PCB components. Some of these factors can be addressed with proper design and layout techniques, such as using a ground plane, using decoupling capacitors, shielding components, and designing the circuit with a high degree of component isolation.
Internal sources of EMI can include clock circuits, switching transistors, and power supplies. They generate EMI through rapid changes in current or voltage. In order to reduce EMI, these components should be operated at low-impedance, with the maximum frequency of operation being much lower than the minimum operating frequency.
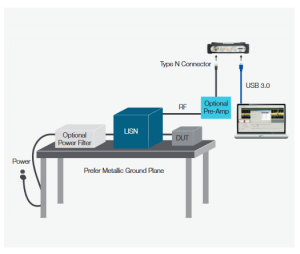
How to Ensure EMI/EMC Compliance in RF Circuit Boards
Another common source of EMI is signal reflection and crosstalk. To reduce this, the width of signal traces should be at least three times larger than their center conductor width. Signals should also be kept separate, and analog signals should be kept away from digital ones to avoid interference. It is also important to minimize signal loops, which can act as antennae and cause unwanted EMI emissions.
Proper trace routing is also critical to minimizing EMI/EMC issues. This includes using wide, low-impedance power traces for power distribution and RF signal return paths, as well as shortening the distance of the return path to reduce loop area and inductance. It is also important to minimize signal reflection and ringing, which can be done by keeping signals separate and routing them in a direct manner.
Other EMI/EMC mitigation techniques can include shielding the entire circuit in a metal enclosure, which provides a low-impedance path for EMI currents to travel and helps to decrease noise. Decoupling capacitors can also help reduce noise, as they provide a low-impedance path to ground for high-frequency noise. They should be located close to the ICs they are decoupling, and should be chosen with a SRF that is close to the noise frequency.
Ultimately, the simplest way to ensure EMI/EMC compliance in RF circuit boards is to use a qualified supplier that offers PCB assembly, wire harness assembly and box-build services with the required capacity and certifications. By selecting a qualified supplier, you can ensure your rf circuit board has the best possible chance of meeting EMI/EMC compliance requirements and avoiding costly delays in the production process. EMSxchange can help you select the right Printed Circuit Board, PCB Assembly, cable & wire harness assembly and box-build suppliers for your EMI/EMC requirements.